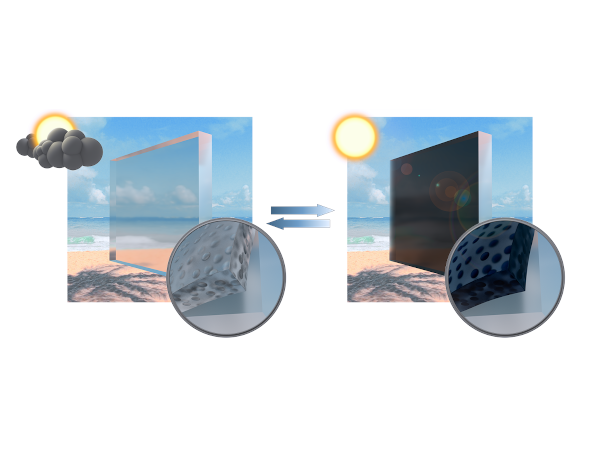
Buildings are responsible for a large portion of the global energy consumption and CO2 emissions in developed countries. Part of it is related to the increasing use of cooling/heating systems, more and more required to balance the energy losses occurring in modern buildings characterized by transparent glazed envelops (i.e., windows). Herein we will show some proposed solutions based on novel nanomaterials-based photoactive films and coatings that are aimed to convert the windows, the weakest point in terms of energy-efficiency of a building, into smart elements (smart windows) that allow not only reducing energy consumptions, but also to collect solar light and convert it into usable energy. We believe that these materials will help reducing the CO2 emissions caused by buildings.
Currículum Vitae
Dr. Claudio Roscini (PhD in Chemistry, UK) is senior researcher at the Catalan Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (ICN2, Spain), where he develops photoactive and chromogenic organic nanomaterials that change their optical properties (e.g. color, luminescence) upon application of external stimuli (e.g., light, temperature). His research characterizes for spanning from the fundamental demonstration of new concepts to the realization of working prototypes, closer to final products. Among other applications, he aims to integrate these nanomaterials in smart windows, optical sensors and security inks. Apart from publications in peer-reviewed journals and several patents, he is cofounder and CTO/CSO of two spinoff companies, Futurechromes (since 2014), and Distinkt (since 2022), aimed to exploit two developed technologies in smart glass and security inks, respectively.

Presencial (C/hospital,64) + Emisión YOUTUBE
Imagen representativa de ventanas inteligentes
Dr. Claudio Roscini (ICN2-CSIC)